Abstract
Background:
Development of inhibitory alloantibodies, commonly known as "inhibitors," against exogenously infused factor VIII (FVIII) is the most significant complication of hemophilia therapy. The aim of this study was to understand the epidemiology of inhibitors in persons with severe hemophilia A (PWHA) in the United States using a national database, the Community Counts Registry for Bleeding Disorders Surveillance.
Methods:
The Community Counts Registry collects detailed medical information on patients with bleeding disorders who receive treatment within the US Hemophilia Treatment Center Network (USHTCN). Patients with severe hemophilia A with (PWHA-I) and without an inhibitor (PWHA-NI) enrolled in the registry between 12/1/2013 and 7/9/2018 were included in this cross-sectional exploratory analysis. PWHA designated as having an unknown history of inhibitor were excluded. Data elements included basic demographics (age, sex/gender, race, ethnicity, employment, insurance status), clinical characteristics (age of diagnosis, treatment characteristics), inhibitor characteristics (age at detection, inhibitor-specific treatments, titers, status), and outcome data (bleeding events, joint disease and procedures, intracranial hemorrhage, ED visits, hospitalizations, chronic pain, opioid use, and days missed from school/work). Data were categorized with reported frequencies, and comparisons between PWHA-I and PWHA-NI were made using Chi-square tests.
Results:
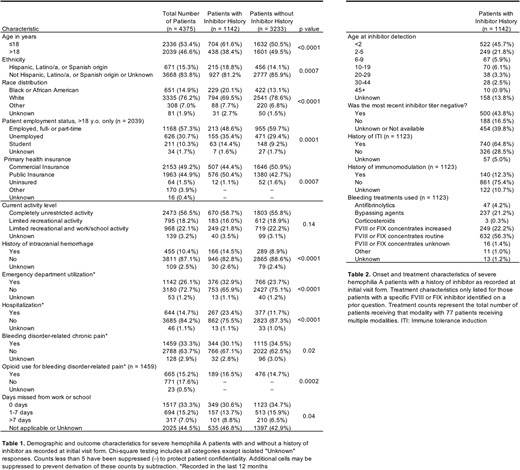
Of 4375 patients with severe hemophilia A, 1142 (26.1%) had a reported history of inhibitor. Among the cohort were 13 (0.30%) female and 7 (0.16%) transgender patients. PWHA-I and PWHA-NI were similarly distributed among sex/gender categories. PWHA-I were more frequently Hispanic, Latino/a, or Spanish origin or black or African American and less frequently white. Nearly all patients were insured, although PWHA-I more frequently utilized public insurance as opposed to commercial insurance as primary insurance, which may align with the lower rate of employment among PWHA-I (Table 1).
PWHA-I more frequently reported a history of intracranial hemorrhage. Notably, no association was identified between inhibitor history and history of joint bleed, history of invasive joint procedure, or limitations of activity level at the time of assessment. During the 12 months prior to assessment, a lower percentage of PWHA-I reported hemophilia-related chronic pain, but those PWHA-I with chronic pain reported opioid use at a modestly increased rate. PWHA-I were more frequently seen in the emergency department and hospitalized than PWHA-NI during the 12 months prior to reporting, and PWHA-I reported more days missed from work or school (Table 1).
Within the PWHA-I cohort, 45.7% of patients had inhibitors detected prior to age 2 years. The majority (64.8%) of PWHA-I had a history of immune tolerance induction and 56.3% reported using routine doses of FVIII concentrates to treat bleeding events. Bypassing agents and increased FVIII concentrates were each used for ~20% of PWHA-I (Table 2).
Conclusions:
This study provides an estimate of the burden of inhibitors in persons with severe hemophilia A in the US, representing approximately 52.9% of all severe hemophilia A patients treated in the USHTCN (CDC, unpublished data). History of an inhibitor reduced patient productivity and increased ED and hospital utilization. Future efforts will focus on a longitudinal analysis of this cohort to better understand the natural history and outcome of inhibitors and their impact on patient quality of life and health care utilization.
Acknowledgments:
This study was performed with the advice of the Community Counts Inhibitor Interest Group and was supported by funds from an ASH HONORS Award for Mr. Sande.
Payne:Shire: Other: treatment product donation; Genentech: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bayer: Other: treatment product donation; Bioverativ: Other: treatment product donation; Novo Nordisk: Other: treatment product donation. Kempton:Novo Nordisk: Research Funding; Genetech, Inc: Honoraria, Research Funding; Shire: Honoraria; Bayer AG: Honoraria; Spark Therapeutics: Honoraria; Grifols: Honoraria; Catalyst Biosciences: Honoraria. Manco-Johnson:CSL Behring: Honoraria; Novo Nordisk: Honoraria; Biogentek: Honoraria; Bayer AG: Honoraria, Research Funding; Baxalta, now part of Shire: Honoraria. Sharathkumar:CSL Behring: Honoraria; Shire: Honoraria; Bayer: Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal